What is Raw Disk Mapping:
Raw Disk Mapping (RDM) is a concept that holds a significant place in the world of virtualization and storage technologies. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of RDM, exploring what it is, its benefits, when to use it, how to set it up, and much more.
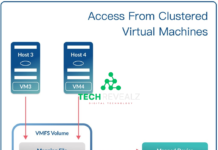
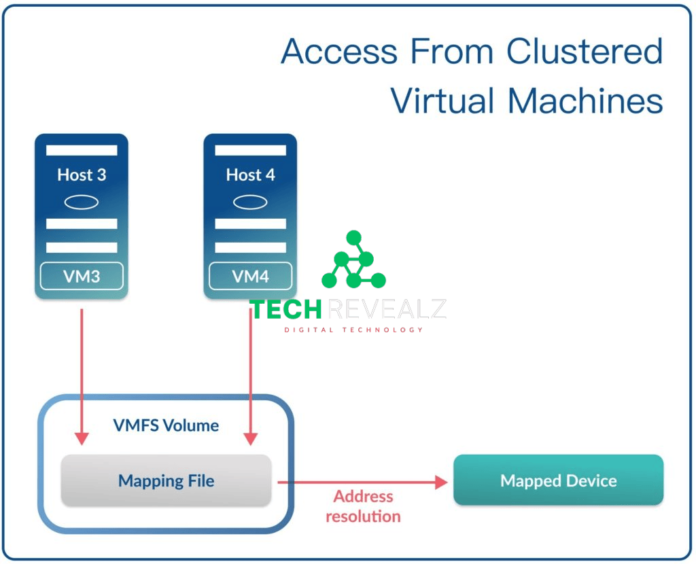
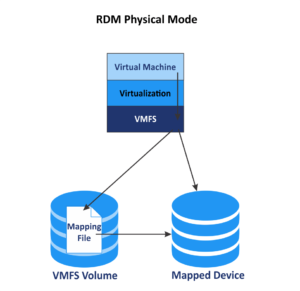
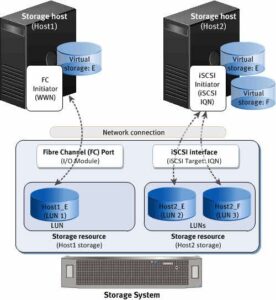
Raw Disk Mapping, often referred to as RDM, is a feature in virtualization environments, such as VMware and Hyper-V. It allows a virtual machine (VM) to directly access and interact with a physical storage device, bypassing the virtual disk file (VMDK in the case of VMware). In simpler terms, it bridges the gap between the VM and the physical disk. Also, Read about Node in Networking
Benefits of Raw Disk Mapping
RDM offers several advantages for virtualized environments. The most notable benefits include:
1. Improved Performance
By bypassing the virtual disk layer, RDM can provide improved I/O performance. This is particularly beneficial for applications that demand high disk throughput.
2. Compatibility with Virtual Machines
RDM allows for more flexibility in virtual machine configurations. It can be particularly useful when dealing with legacy applications that require direct access to physical storage.
When to Use Raw Disk Mapping
RDM is not a one-size-fits-all solution. You should consider using RDM when:
1. Direct Disk Access is Necessary
When certain applications or services require direct access to physical disks, RDM becomes a crucial feature.
2. Compatibility is Essential
If you’re working with legacy systems or applications that are not compatible with virtual disk files, RDM can bridge the compatibility gap.
Setting up Raw Disk Mapping
Configuring RDM can vary depending on the virtualization platform you’re using. However, the general steps involve:
- Identifying the physical disk you want to map.
- Creating an RDM disk on your VM.
- Mapping the physical disk to the VM.
- Formatting and partitioning the mapped disk within the virtual machine.
Risks and Considerations
While RDM offers several benefits, it’s important to be aware of the risks and considerations associated with its use. These include:
- Complexity: Setting up RDM can be more complex than using virtual disks, and it might require advanced knowledge of the virtualization platform.
- Limited Snapshot Support: Some virtualization platforms have limited or no support for snapshots when RDM is used.
Raw Disk Mapping vs. Virtual Disk
It’s important to note the distinction between RDM and virtual disk usage. While RDM provides direct access to physical storage, virtual disks are files hosted on a data store. The choice between the two depends on your specific requirements and compatibility.
Use Cases for Raw Disk Mapping
RDM finds its application in various scenarios, including:
- Database Servers: Databases often benefit from RDM as they require low-latency and high-performance access to storage.
- Clustering: For applications that require clustering, RDM may be the preferred choice to ensure data consistency and synchronization.
Best Practices for Raw Disk Mapping
To make the most out of RDM, consider these best practices:
- Always document your RDM configuration for future reference.
- Regularly monitor the performance of RDM-enabled VMs to ensure optimal results.
- Keep your virtualization platform up to date to benefit from the latest RDM improvements and bug fixes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Raw Disk Mapping is a powerful feature in virtualization environments that allows direct access to physical storage devices, enhancing performance and compatibility for virtual machines. However, it should be used judiciously, considering the specific requirements of your applications and the complexity involved in its setup.
FAQs
-
What is the main advantage of Raw Disk Mapping (RDM)?
- The primary advantage of RDM is improved I/O performance by allowing virtual machines to access physical storage directly.
-
When should I consider using Raw Disk Mapping?
- RDM is recommended when applications require direct access to physical disks or when compatibility with legacy systems is essential.
-
Are there any risks associated with Raw Disk Mapping?
- Yes, some risks include complexity in setup and limited snapshot support in certain virtualization platforms.
-
How does Raw Disk Mapping differ from virtual disks?
- Raw Disk Mapping provides direct access to physical storage, while virtual disks are files hosted on a data store within a virtualization platform.
-
What are some common use cases for Raw Disk Mapping?
- RDM is commonly used for database servers and clustering applications where low-latency access to storage is crucial.